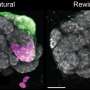
BREAKING: Researchers at Helmholtz Munich, the Technical University of Munich, and the LMU University Hospital Munich have made a groundbreaking discovery that could change the landscape of dementia treatment. A new study reveals that a single enzyme failure drives the loss of nerve cells in dementia through a process known as ferroptosis. This urgent finding sheds light on a previously unknown mechanism contributing to neurodegeneration in the human brain.
This research is particularly critical as it offers the first molecular evidence linking ferroptosis directly to neuron loss, a revelation that could pave the way for innovative therapies aimed at combating severe early-onset childhood dementia.
The study, released on October 11, 2023, demonstrates how the malfunction of this enzyme leads to irreversible damage to nerve cells, prompting a call for immediate attention to potential therapeutic strategies. The implications of this work are staggering; it not only enhances our understanding of dementia but also provides a clear target for future drug development.
Why This Matters NOW: With dementia cases on the rise globally, affecting millions of families, this discovery provides a beacon of hope. Understanding how ferroptosis accelerates neuron loss can significantly alter the approach to treatment and prevention, particularly for young patients facing early cognitive decline.
As the research community races to explore these findings further, experts believe this could be the key to unlocking new, life-altering treatments. The urgency of this research is underscored by the pressing need for effective therapies in a field that has seen limited progress in recent years.
What’s Next: Ongoing studies will focus on how to inhibit ferroptosis effectively and whether existing drugs can be repurposed to protect nerve cells from this damaging process. Researchers are calling for collaboration across institutions to fast-track the development of potential therapies.
Stay tuned for updates as this story develops, and share this vital information to raise awareness about the fight against dementia. The future of treatment may hinge on these critical insights.