BREAKING: New research has just revealed critical insights into the application of artificial intelligence in medical imaging, prompting experts to advise caution in its use. The study, published in the journal Biomedical Optics Express, highlights the potential pitfalls of an AI method known as virtual staining, which may not always enhance the quality of medical images as previously believed.
This urgent update comes from a team at the Center for Label-free Imaging and Multiscale Biophotonics (CLIMB) at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, led by Sourya Sengupta. Researchers found that while virtual staining can improve image usability in some contexts, it may actually hinder the accuracy of medical assessments in others. “AI can be a great tool—it does help in some cases—but you have to be a little bit cautious,” Sengupta cautioned.
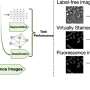
The study investigates the effectiveness of virtual staining against traditional methods, particularly in tasks such as cell segmentation and classification. Using the innovative Omni-Mesoscope imaging system, researchers generated extensive datasets comparing label-free images, virtually stained images, and fluorescent stained images. These comparisons are crucial for validating the practical applications of AI in clinical settings.
In a striking revelation, the research indicates that virtually stained images performed significantly worse when analyzed by high-capacity networks, which are designed to discern complex relationships within data. For segmentation tasks, virtually stained images matched the performance of label-free images. However, in cell classification tasks—critical for assessing drug efficacy—virtually stained images fell short, suggesting that AI may obscure vital information necessary for accurate diagnostics.
“Even if AI is a buzzword now, you have to be cautious when applying it in sensitive domains like biomedical imaging and healthcare,” Sengupta reiterated, emphasizing the need to verify AI’s effectiveness based on the specific context.
The implications of this research are profound, as medical imaging is pivotal in diagnosing diseases and monitoring treatments. The findings urge healthcare professionals to carefully assess the application of AI technologies, ensuring they truly enhance clinical outcomes rather than complicate them.
As AI continues to evolve, this study serves as a timely reminder of the balance required between technological advancement and practical application in healthcare. Researchers and clinicians are now called to review their workflows and consider the real-world implications of deploying AI tools like virtual staining.
Stay tuned for more updates on this developing story as the medical community responds to these significant findings.