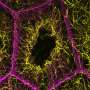
A recent study from Northwestern Medicine has provided significant insight into the complex processes of cellular construction, specifically how cells create the internal scaffolding necessary for healthy egg development. Published in the Journal of Cell Biology, this research explores the coordinated roles of two essential structural systems: actin and microtubules.
Understanding how egg cells are formed is crucial not only for developmental biology but also for reproductive health. The research highlights that actin, a protein that forms microfilaments, and microtubules, which are part of the cytoskeleton, work synchronously to establish the necessary architecture for developing oocytes.
Actin and Microtubules: The Building Blocks
Egg cell development is a highly intricate process. Researchers discovered that actin provides the foundational support, while microtubules deliver stability and transport cellular materials. This combination creates a robust scaffolding system that ensures the proper shape and functionality of the egg cells.
In the study, scientists conducted experiments to observe how these two systems interact. They found that disruptions in either actin or microtubule function led to significant abnormalities in egg cell structure. This finding underscores the importance of both components in maintaining cellular integrity during the early stages of development.
The implications of this research extend beyond basic biology. Understanding the mechanisms behind egg cell formation can lead to advancements in fertility treatments and reproductive technologies. As scientists continue to unravel these cellular mysteries, the potential for improving reproductive health becomes increasingly tangible.
Future Research Directions
The study opens new avenues for exploration in cellular biology. Researchers plan to further investigate how these structural systems can be manipulated to enhance egg cell viability. With fertility issues affecting a substantial percentage of the population, findings from this research could have far-reaching effects.
Moreover, the collaboration among various disciplines, including cell biology and reproductive medicine, is essential for translating these findings into practical applications. As the scientific community delves deeper into the functions of actin and microtubules, the hope is to uncover additional strategies for addressing fertility challenges.
In summary, the groundbreaking study from Northwestern Medicine highlights the intricate dance between actin and microtubules in the construction of healthy egg cells. As research continues, the potential to translate these discoveries into real-world solutions for reproductive health remains a key focus for scientists.