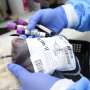
A recent study has provided valuable insights into the commercial implementation of gene therapies for sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia. This research, presented at the 67th ASH Annual Meeting and Exposition held from December 6 to 9, 2023, in Orlando, Florida, aims to inform best practices for manufacturers and medical centers as they prepare to meet the increasing demand for these innovative treatments.
The study emphasizes the importance of real-world data in understanding the challenges and opportunities associated with the roll-out of gene therapies. As the healthcare landscape evolves, stakeholders are keen to learn from experiences in the field to enhance patient access and treatment outcomes.
Understanding the Demand for Gene Therapies
With advancements in gene therapy, there is a growing expectation for therapies that address genetic disorders effectively. Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia affect millions globally, creating urgent public health needs. As manufacturers race to develop and distribute these therapies, understanding the market landscape becomes critical.
The research highlights key factors influencing the successful implementation of gene therapies. Issues such as healthcare infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, and reimbursement policies play significant roles in determining how quickly these treatments can reach patients. The study’s findings suggest that collaboration among manufacturers, healthcare providers, and policymakers is essential to streamline processes and mitigate barriers.
Data collected during the study revealed that early adopters of gene therapies have experienced varying levels of success. For instance, some medical centers reported substantial improvements in patient outcomes, while others faced logistical challenges. Learning from these experiences can help refine strategies for wider adoption.
Best Practices for Future Roll-Outs
As the demand for gene therapies increases, best practices derived from this study can guide future initiatives. The researchers recommend that manufacturers and medical centers prioritize patient education and engagement. Ensuring that patients and caregivers understand the benefits and risks associated with gene therapies can significantly impact treatment adherence and overall satisfaction.
Moreover, the study calls for a more robust dialogue between stakeholders to align expectations and resources. By fostering partnerships among healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, and regulatory agencies, the path to implementing these therapies can be significantly smoothed.
The findings from the ASH meeting underscore the necessity of ongoing research and adaptation in the field of gene therapies. As new data emerges, continuous evaluation and adjustment of strategies will be crucial to enhance patient care and ensure equitable access to these groundbreaking treatments.
In conclusion, the insights from this study serve as a roadmap for the future of gene therapies for sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia. By leveraging real-world experiences and fostering collaboration, stakeholders can work towards a more effective and accessible healthcare solution for those in need.