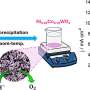
The development of a new semicrystalline catalyst marks a significant advancement in the efficiency of hydrogen production through water electrolysis. This innovative catalyst addresses the challenges posed by the oxygen evolution reaction (OER), which has long hindered the process due to its high energy requirements and operational conditions. Research indicates that this new approach provides a viable pathway toward achieving emission-free and sustainable energy technologies.
Water electrolysis is a promising method for generating clean hydrogen, a key component in the transition to greener energy sources. The OER is a critical reaction in this process, yet it typically demands a high potential energy input and operates under highly oxidative conditions. These factors often lead to a difficult balance between catalytic activity and long-term stability, which has been a barrier to widespread adoption.
The newly developed semicrystalline catalyst enhances the efficiency of the OER by optimizing the balance between these two critical factors. By improving catalytic activity while maintaining stability over extended periods, this catalyst could significantly decrease the energy costs associated with hydrogen production. According to the latest study, the catalyst demonstrates remarkable potential in laboratory settings, making it a strong candidate for future applications in sustainable energy systems.
Implications for Sustainable Energy
The implications of this research extend beyond laboratory results. With the ongoing global shift towards sustainable energy, efficient hydrogen production is essential. Clean hydrogen can serve as a crucial energy carrier, enabling the storage and transportation of renewable energy sources. This development could help nations reduce their carbon footprints and meet emission reduction targets set in international agreements.
The researchers behind this catalyst highlight the potential for scalable applications. By integrating this technology into existing electrolysis systems, industries could significantly enhance their hydrogen output while minimizing energy consumption. The transition to a more sustainable energy landscape hinges on innovations like these, which facilitate the use of renewable resources in hydrogen production.
Future Research Directions
While the initial results are promising, further research is necessary to understand the long-term performance of the semicrystalline catalyst in real-world conditions. Questions remain regarding its durability and effectiveness when exposed to various operational environments. Future studies will need to explore these aspects to ensure that the catalyst can perform reliably in commercial applications.
The development of this catalyst is a vital step towards realizing the full potential of electrolytic hydrogen production. As researchers continue to refine their methods and understand the intricate dynamics of the OER, the path forward for clean hydrogen production becomes clearer. Innovations such as this not only represent technological progress but also signify a commitment to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
In summary, the semicrystalline catalyst stands out as a promising solution for enhancing both activity and stability in the hydrogen production process. As the world shifts towards greener energy solutions, advancements in this area will be crucial in unlocking the full potential of hydrogen as a clean energy source.