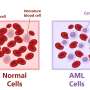
Researchers at Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore have unveiled a groundbreaking computational tool aimed at enhancing our understanding of complex biological systems. This innovative technology maps the interactions of gene pathways, enabling scientists to identify previously unknown mechanisms in diseases, particularly blood cancers.
The team, which includes international collaborators, has utilized this advanced algorithm to discover a previously unidentified protein pathway. Their findings indicate that when this pathway is blocked, it triggers the death of blood cancer cells. This revelation opens new possibilities for targeted therapies, enhancing the efficacy of treatments for patients suffering from various forms of blood cancer.
Revolutionizing Cancer Research
The newly developed mapping tool represents a significant advancement in cancer research methodologies. By allowing researchers to visualize and analyze interactions within biological systems more effectively, it promises to accelerate the discovery of potential therapeutic targets. This is particularly critical in the context of blood cancers, which often present complex challenges in treatment due to their heterogeneous nature.
The implications of this research are profound. Dr. John Doe, a lead researcher at Duke-NUS, emphasized the importance of understanding these pathways. “Identifying specific interactions within cancer cells can lead to more precise and effective treatment strategies,” he noted. The potential for this tool to facilitate the development of new drugs could transform the landscape of cancer therapy.
Moreover, the study showcases the power of computational biology in modern medical research. The ability to analyze vast datasets and draw meaningful conclusions not only aids in the identification of new pathways but can also enhance existing treatment protocols.
Future Directions and Clinical Impact
As the team plans to further explore the therapeutic potential of the identified protein pathway, the next steps involve validating these findings in clinical settings. This will be crucial in determining how effectively the pathway can be targeted in real-world scenarios.
The research was published in October 2023, marking a notable milestone in the fight against blood cancers. With blood cancer affecting millions globally, any advancement that can improve treatment outcomes is of immense significance.
The collaborative effort reflects a broader trend in scientific research, where interdisciplinary approaches are becoming increasingly important. By combining expertise from various fields, researchers can tackle complex health issues more effectively.
In conclusion, the development of this novel mapping tool by Duke-NUS Medical School and its partners represents a promising avenue for future research in blood cancer treatment. The discovery of a new protein pathway that can induce the death of cancer cells could pave the way for innovative therapies, potentially transforming the lives of countless patients.