A team of researchers from China has introduced a groundbreaking artificial intelligence framework named DrugCLIP, which has the potential to revolutionize the discovery of life-saving medicines. This innovative technology can rapidly analyze millions of possible drug compounds against thousands of protein targets in a matter of hours, achieving speeds that are ten million times faster than traditional virtual screening methods.
The implications of DrugCLIP are profound, particularly in the context of global health challenges. As the world continues to grapple with emerging diseases and the need for effective treatments, this new AI tool could significantly reduce the time and resources required to identify promising drug candidates. The researchers assert that this acceleration in the drug discovery process could lead to quicker responses to public health emergencies.
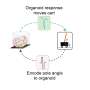
How DrugCLIP Works
The framework utilizes advanced algorithms to sift through vast databases of chemical compounds. By employing deep learning techniques, DrugCLIP identifies optimal matches between drug candidates and specific protein targets associated with various diseases. This method streamlines a typically lengthy process, allowing researchers to focus on the most viable options for further development.
According to the research team, the AI framework can handle complex datasets that would take conventional methods weeks or even months to analyze. This efficiency not only saves time but also reduces costs associated with drug development, which can reach billions of dollars for pharmaceutical companies.
The researchers conducted extensive tests to validate DrugCLIP, demonstrating its accuracy and reliability. Their findings suggest that the AI framework can enhance the identification of compounds that might otherwise be overlooked in traditional drug discovery approaches.
Potential Impact on Global Health
The introduction of DrugCLIP aligns with a growing trend towards the integration of artificial intelligence in healthcare. As the technology continues to evolve, its applications may expand beyond drug discovery into areas such as diagnostics and personalized medicine. The potential for AI to improve patient outcomes is significant, particularly in regions with limited access to advanced medical resources.
While the full impact of this development remains to be seen, the researchers emphasize the importance of collaboration between AI experts and medical professionals. They believe that by working together, the scientific community can harness the power of DrugCLIP to tackle some of the most pressing health issues facing society today.
As DrugCLIP undergoes further testing and refinement, its creators hope to see it adopted by pharmaceutical companies and research institutions worldwide. This AI framework could mark a pivotal shift in how medicines are discovered, potentially leading to faster treatment options for patients in need.
In conclusion, the unveiling of DrugCLIP represents a significant advancement in the intersection of technology and healthcare. As researchers continue to explore its capabilities, the promise of more efficient drug discovery could change the landscape of medicine, paving the way for innovations that save lives.