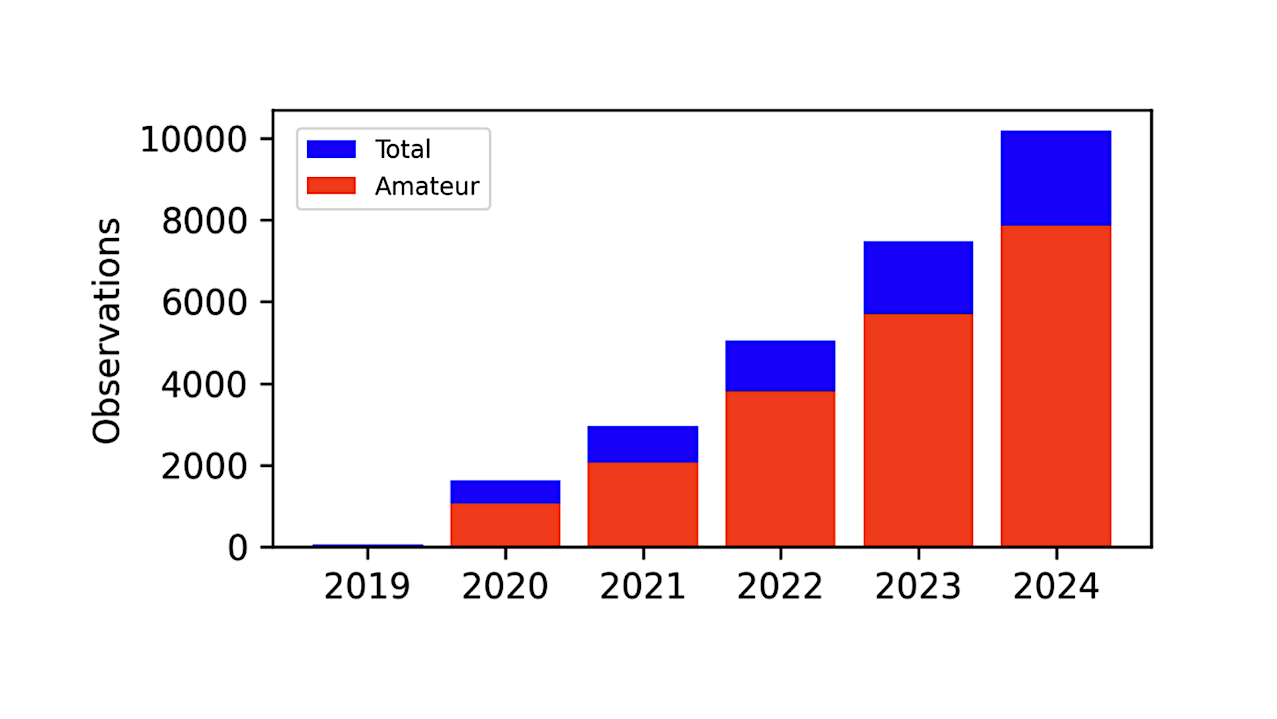
Research in neuroscience has made significant strides in 2025, unveiling insights that could transform our understanding of brain health and aging. Studies conducted by various international teams have highlighted effective strategies for maintaining cognitive function and reducing inflammation in the body, particularly in relation to joint health.
One of the standout findings this year focuses on the concept of neuroplasticity, which refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. According to a study published in the *Journal of Neuroscience*, researchers have identified specific lifestyle changes that can enhance neuroplasticity, potentially leading to improved cognitive function as individuals age. This research emphasizes that engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and practicing mindfulness can significantly contribute to brain health.
Additionally, new approaches to inflammation management have emerged from studies conducted by health professionals at institutions such as the University of Sydney. Their research revealed that certain anti-inflammatory diets could not only alleviate joint pain but also positively impact brain function. The findings suggest that dietary adjustments could play a crucial role in minimizing inflammation, which is linked to various neurological disorders.
Innovative Strategies for Healthy Aging
In a groundbreaking study released in July 2025, researchers from Stanford University explored the effects of cognitive training programs on older adults. The trial involved over 1,000 participants aged 60 and above, aiming to assess the impact of targeted cognitive exercises on memory retention and mental agility. Results indicated a remarkable 30% improvement in cognitive performance among those who engaged in the training, demonstrating the potential for such programs to combat age-related cognitive decline.
Moreover, researchers have emphasized the importance of social engagement and mental challenges in promoting brain health. Activities that stimulate the mind, such as puzzles, reading, or learning a new language, are not only enjoyable but can also serve as protective factors against cognitive decline. The findings underscore the notion that keeping the mind active is just as vital as physical health in the aging process.
Global Implications and Future Directions
The implications of these findings extend beyond individual health, suggesting a need for public health initiatives aimed at promoting brain health across communities. As the global population ages, the demand for effective strategies to maintain cognitive function and overall health will only increase.
As researchers continue to explore the intricate workings of the human brain, the global scientific community remains hopeful that these advancements will lead to practical applications in healthcare. The year 2025 has proven to be pivotal in neuroscience, laying the groundwork for future research and potential therapeutic interventions.
In conclusion, the latest research in neuroscience not only sheds light on how to keep our brains young but also offers actionable insights into reducing inflammation and enhancing cognitive function. These findings have the potential to transform how we approach aging and overall health, prompting both individuals and health professionals to prioritize brain health in their daily lives.