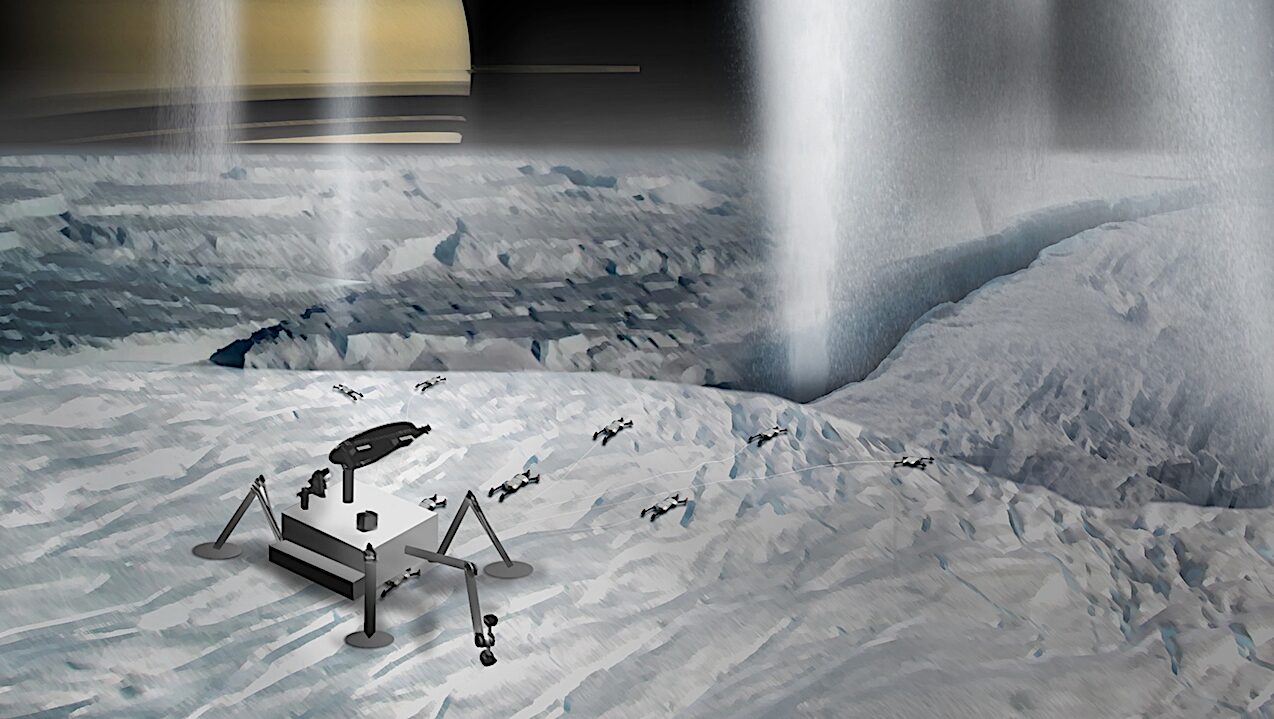
Recent research has established a roadmap for future missions to the icy moon Enceladus, a prime candidate for astrobiological exploration. The findings are documented in a comprehensive paper that outlines key hypotheses to guide upcoming investigations during the current decadal cycle and beyond. Enceladus is considered a high-priority target due to its possession of the essential ingredients for life: organic materials, a liquid solvent, and an energy source.
This prioritization is affirmed in the 2023–2032 Planetary Science and Astrobiology Decadal Survey published by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. The report lists Enceladus as a destination for a NASA New Frontiers class mission and recommends the development of an Enceladus Orbilander mission as the second priority Flagship mission.
In 2021, the science definition team for the proposed Enceladus Vent Explorer, part of NASA’s Innovative Advanced Concepts program, conducted three workshops to identify critical scientific inquiries regarding Enceladus. These discussions led to the formulation of two primary science goals: first, to investigate how the thermal evolution of Enceladus has influenced its capacity to maintain a liquid ocean and recycle nutrients; second, to explore how the moon’s astrobiological potential has evolved over time.
Key Hypotheses and Investigative Objectives
The paper outlines various investigations that will address these pivotal science goals. By detailing the scientific background and proposed hypotheses, the researchers aim to establish a comprehensive framework for future explorations. Additionally, they introduce a novel methodology to characterize the organic state of Enceladus, which is crucial for formulating hypotheses about the emergence of life and contextualizing potential biosignatures.
The framework not only provides insights into the moon’s current conditions but also sets the stage for understanding its historical context. Such knowledge could illuminate the broader implications of astrobiological research and enhance our understanding of life beyond Earth.
Furthermore, the authors emphasize the importance of advancing technology and research to facilitate ocean world exploration. They recommend specific developments that could enhance future missions, ensuring that scientists are equipped to investigate the intriguing possibilities that Enceladus presents.
The graphic depiction of the Enceladus Vent Explorer: Phase II concept illustrates the ambitious scope of this project, highlighting the potential for groundbreaking discoveries in astrobiology and planetary science. As researchers continue to refine their hypotheses and investigative objectives, the prospect of unraveling the mysteries of this enigmatic moon grows closer.
In conclusion, the new roadmap for Enceladus exploration marks a significant step forward in our quest to understand the potential for life beyond our planet. With ongoing advancements in technology and a clear set of scientific goals, future missions promise to shed light on one of the most compelling locations in our solar system.