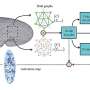
A groundbreaking study has unveiled how a deep-learning model can predict the cellular processes that occur during the early development of fruit flies. This innovative approach allows researchers to observe how tissues and organs form through the dynamic interactions of thousands of cells.
The research, conducted by a team at the University of Cambridge, focuses on the intricate transitions that cells undergo as they differentiate and proliferate. The findings, published in 2023, could significantly enhance our understanding of developmental biology and improve models for studying similar processes in other organisms.
Unveiling the Mechanisms of Development
During the early stages of development, fruit flies exhibit remarkable cellular transformations. The deep-learning model developed by the research team analyzes extensive datasets, allowing it to map the complex patterns of cell behavior. This includes the splitting, growing, and shifting of cells that lead to the formation of vital tissues and organs.
By harnessing advanced computational techniques, the model can predict how these cellular changes unfold in real-time. The implications of this research extend beyond fruit flies, potentially offering insights into human development and associated medical conditions.
The study emphasizes the importance of understanding cellular dynamics in developmental processes. With more than 10,000 cells involved in the early stages, the model provides a comprehensive view of how these interactions shape the organism’s future.
Significance and Future Applications
This pioneering work not only highlights the capabilities of artificial intelligence in biological research but also opens the door for future applications in regenerative medicine and developmental disorders. The ability to predict cellular behavior has significant ramifications for fields such as tissue engineering and gene therapy.
According to the research team, the deep-learning model can be adapted and applied to other species, potentially transforming how scientists study growth and development across various biological contexts. The integration of such technology into biological research marks a new era in understanding the fundamental processes of life.
As this research progresses, it may provide essential tools for addressing complex health challenges, further bridging the gap between computational sciences and biology. The implications of these findings could pave the way for advancements that enhance our knowledge of cellular behavior and its impact on health and disease.
In summary, the deep-learning model developed by the University of Cambridge represents a significant leap in our understanding of cellular development. By predicting how fruit flies form, this research not only illuminates fundamental biological processes but also sets the stage for future innovations in medical science.