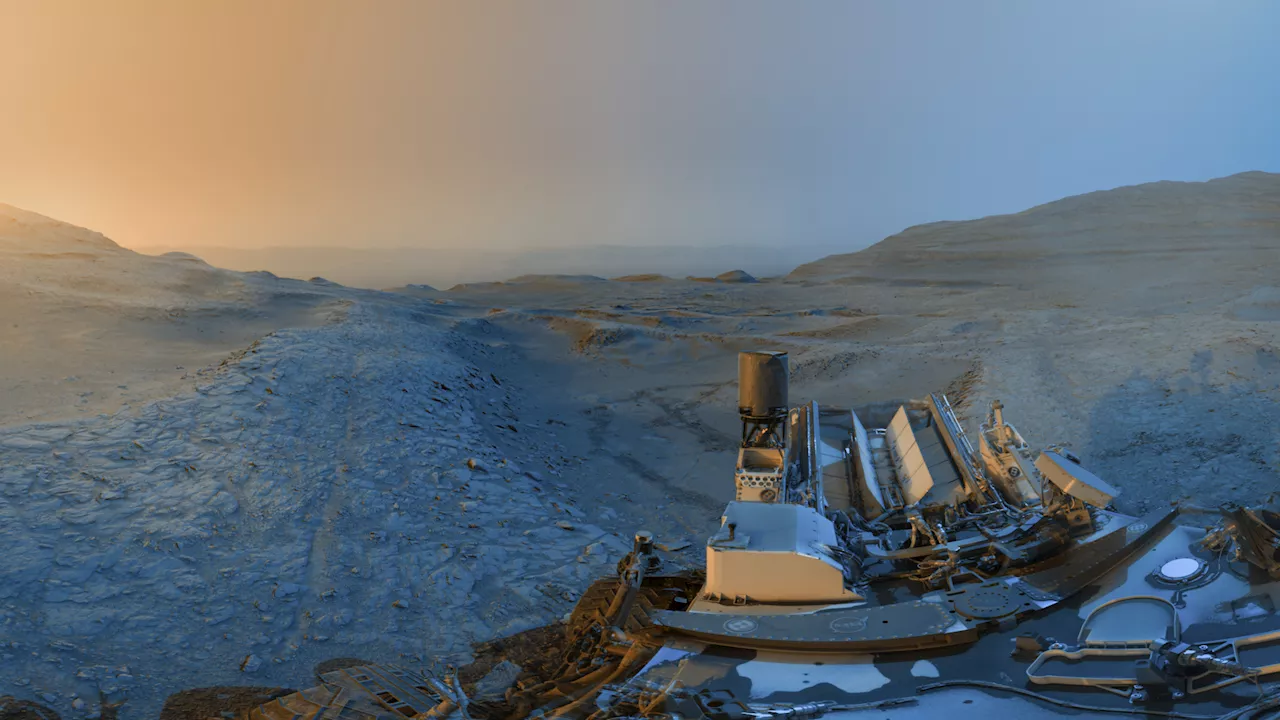
NASA’s Curiosity rover has delivered a breathtaking panorama of the Martian landscape, showcasing the rugged terrain of Mount Sharp within Gale Crater. The images, taken over two separate Martian days in November 2025, highlight the dramatic interplay of light across ancient formations shaped by water, offering valuable insights into the planet’s geological history.
The recent images were captured on Sols 4,722 and 4,723, with the first set taken at 16:15 local Mars time on Sol 4,722, followed by a second set at 08:20 on Sol 4,723. NASA officials explained that merging these two images allows for a richer understanding of the terrain. The photos were enhanced with cool blue and warm yellow hues, illustrating how lighting conditions shift throughout a Martian day. “Adding color to these kinds of merged images helps different details stand out in the landscape,” they noted.
Exploring Ancient Water-Shaped Terrain
The area depicted in the panorama features intricate boxwork formations, which are networks of mineral-rich ridges created by groundwater flowing through cracks in the rock billions of years ago. Over time, wind erosion has worn away the softer material, leaving behind exposed mineral veins. Scientists are particularly interested in these formations, as they contain evidence of ancient water activity and the evolving environmental conditions on Mars.
Curiosity has been diligently studying this region, particularly the boxwork terrain and other sedimentary layers that document Mars’ transition from a potentially habitable, wetter environment to the cold, arid landscape observed today. The rover’s drill, located at the end of its robotic arm, recently collected samples from a site known as “Nevado Sajama,” further contributing to the mission’s scientific output.
The striking panorama not only captures the beauty of the Martian landscape but also allows scientists to analyze rock chemistry, textures, and mineral veins. These details are essential for piecing together the planet’s complex history. The rover’s ability to conduct science observations while maintaining communication with orbiters overhead has made its operations more efficient, maximizing the output from Curiosity’s aging nuclear power source.
Curiosity’s Ongoing Mission
More than 13 years since its arrival on Mars, Curiosity continues to provide both stunning views and critical scientific data. The rover’s mission has demonstrated that, despite the challenges of exploring the Red Planet, it still holds many stories waiting to be uncovered. As technology advances, lower-cost space missions like NASA’s ESCAPADE are also beginning to contribute exciting scientific discoveries, albeit with inherent risks and trade-offs.
The latest images from Curiosity serve as a reminder of the importance of ongoing exploration and the potential for new findings that can reshape our understanding of Mars. As researchers continue to analyze the data collected by the rover, the quest to unravel the planet’s mysteries remains as compelling as ever.