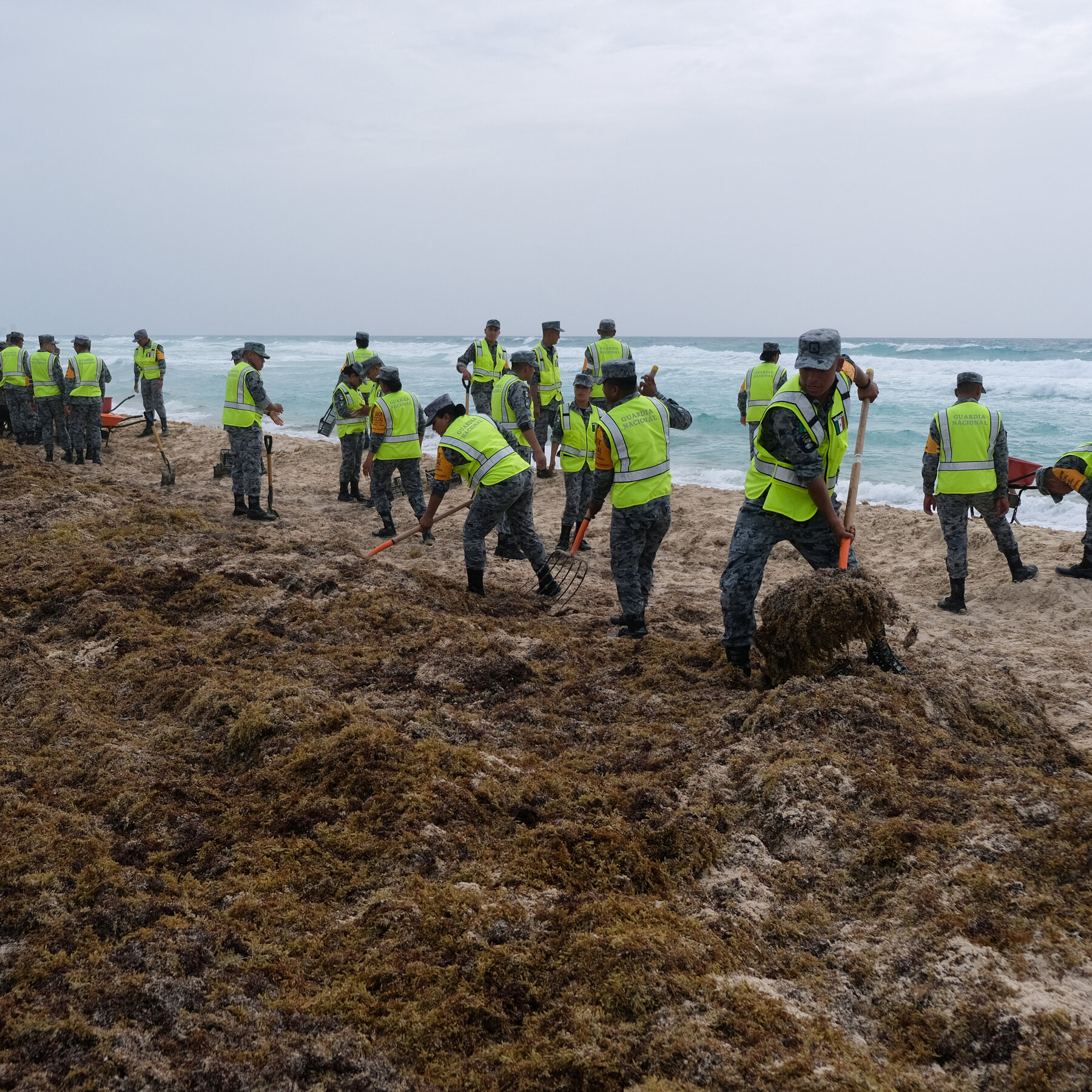
Heavy blooms of yellowish-brown seaweed are disrupting coastlines along the Equator while a historic patch of seaweed in the North Atlantic is rapidly disappearing. This phenomenon is closely linked to climate change and has significant implications for marine ecosystems and coastal communities.
Recent research conducted by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) reveals that the sargassum seaweed, which typically thrives in warmer waters, has expanded dramatically. In 2023, the total area of sargassum blooms reached an astonishing 2 million square kilometers, primarily affecting regions from the Caribbean Sea to the coasts of Florida and the Gulf of Mexico. The sheer volume of this seaweed is resulting in widespread beach closures and significant ecological disturbances.
Disappearance of Historic Seaweed Patch
While new blooms are proliferating, a longstanding patch of sargassum in the North Atlantic has been declining. This patch has been a critical habitat for various marine species for centuries. The loss of this area is concerning not only for biodiversity but also for local fisheries that depend on the health of these ecosystems.
The shift in seaweed populations can be attributed to rising ocean temperatures and increased nutrient runoff from agricultural practices. These conditions create a perfect environment for sargassum to flourish in some areas while simultaneously stressing older patches, leading to their decline.
Impact on Coastal Communities
The impact of these changes is profound for coastal communities reliant on tourism and fishing. Beaches littered with rotting seaweed can deter visitors, affecting local businesses. Furthermore, the blooms can produce harmful gases as they decompose, posing health risks to residents and tourists alike.
Local governments are now faced with the challenge of managing these blooms. Some have initiated clean-up operations, while others are exploring the potential for using sargassum as a resource, such as for fertilizer or biofuel. However, the financial and logistical implications of these measures require careful consideration.
As climate change continues to influence marine ecosystems, understanding the dynamics of sargassum blooms and their impact on coastal areas will be crucial. Ongoing research and monitoring will be essential to mitigate the negative effects and adapt to this shifting environment.
The situation underscores the urgency for international cooperation in addressing climate change and protecting marine ecosystems, which are vital not only for biodiversity but also for the livelihoods of millions worldwide.