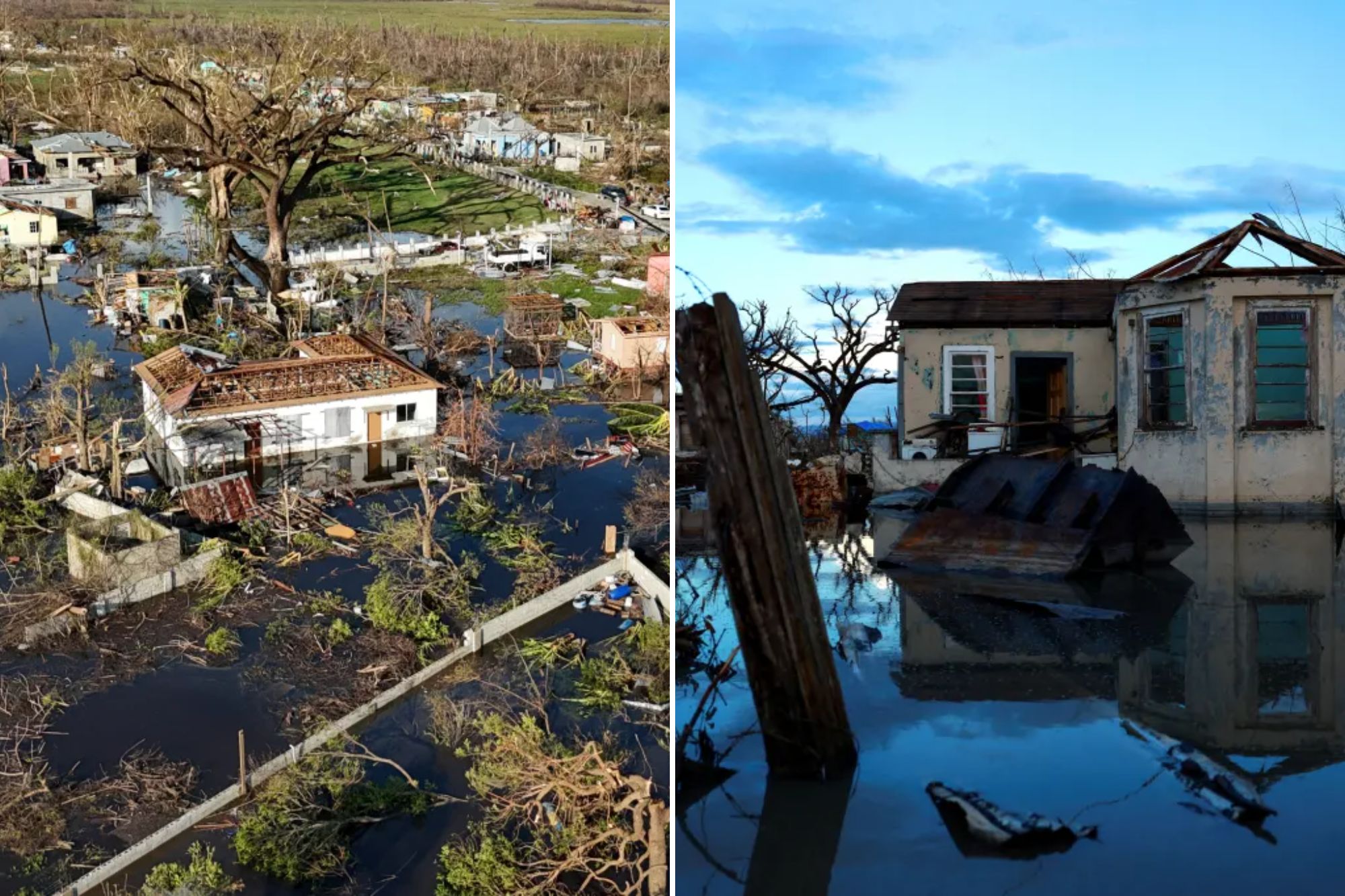
Jamaica is grappling with a leptospirosis outbreak linked to the devastation caused by Hurricane Melissa, which struck the island on October 28, 2023. The Category 5 hurricane brought catastrophic flooding and landslides, unleashing nearly 30 inches (76 cm) of rain and creating conditions conducive to the spread of this bacterial disease. As a result, officials suspect that leptospirosis has caused at least six deaths since the storm.
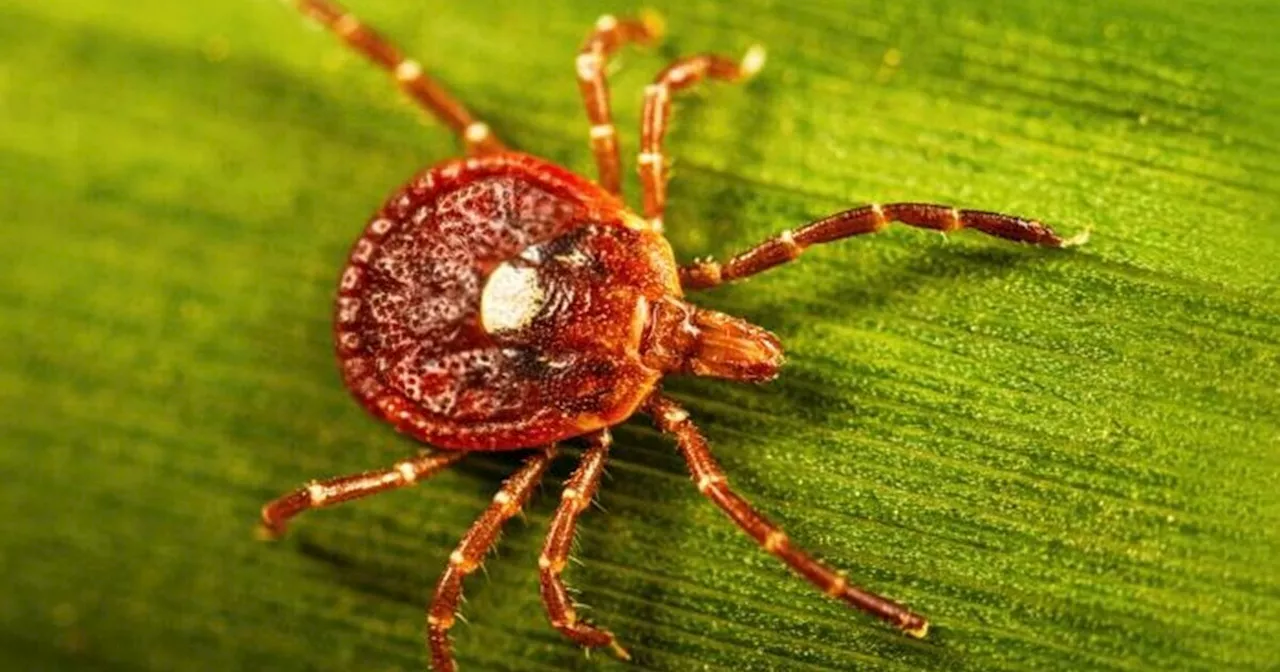
Health Minister Christopher Tufton confirmed on November 24 that between October 30 and November 20, there have been nine confirmed cases of leptospirosis, with an additional 28 suspected cases. The disease is transmitted through water or soil contaminated by the urine of infected animals, particularly rodents. Humans can become infected through cuts in the skin or by ingesting contaminated water.
The initial symptoms of leptospirosis, which include fever, headache, and muscle aches, can easily be mistaken for the flu. Without prompt treatment, the condition can escalate into severe forms, leading to complications such as kidney failure, liver damage, meningitis, and severe internal bleeding.
In a recent press conference, Minister Tufton emphasized the increased risk faced by individuals exposed to contaminated floodwaters. This includes farmers, emergency responders, and others involved in cleanup efforts. “The outbreak follows the passage of the storm which has created conditions that have increased the risk of exposure to contaminated water and soil,” Tufton stated.
The aftermath of Hurricane Melissa has been devastating for Jamaica, with officials estimating damages of approximately $10 billion. The storm severely impacted key sectors, including tourism and agriculture, and damaged nearly 200,000 buildings across the island. As the nation works to recover from both the hurricane and the ensuing health crisis, public health officials are urging vigilance to prevent further spread of leptospirosis.
Authorities continue to monitor the situation closely and provide necessary resources to affected communities. The outbreak serves as a stark reminder of the public health challenges that can arise in the wake of natural disasters, highlighting the need for robust emergency response strategies.