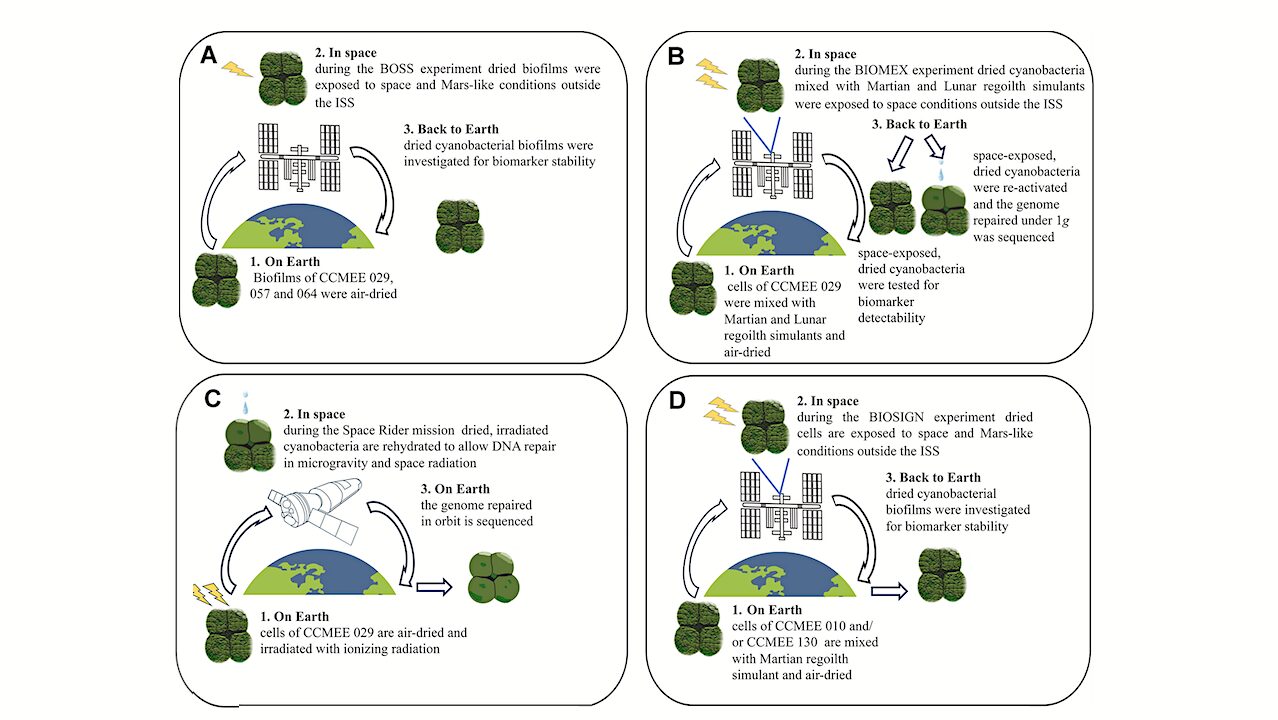
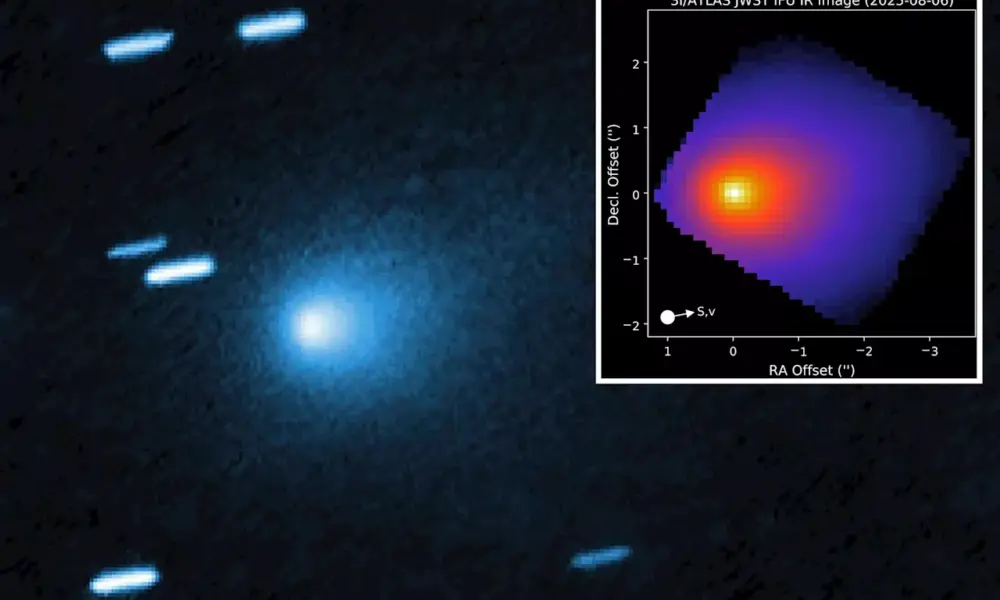
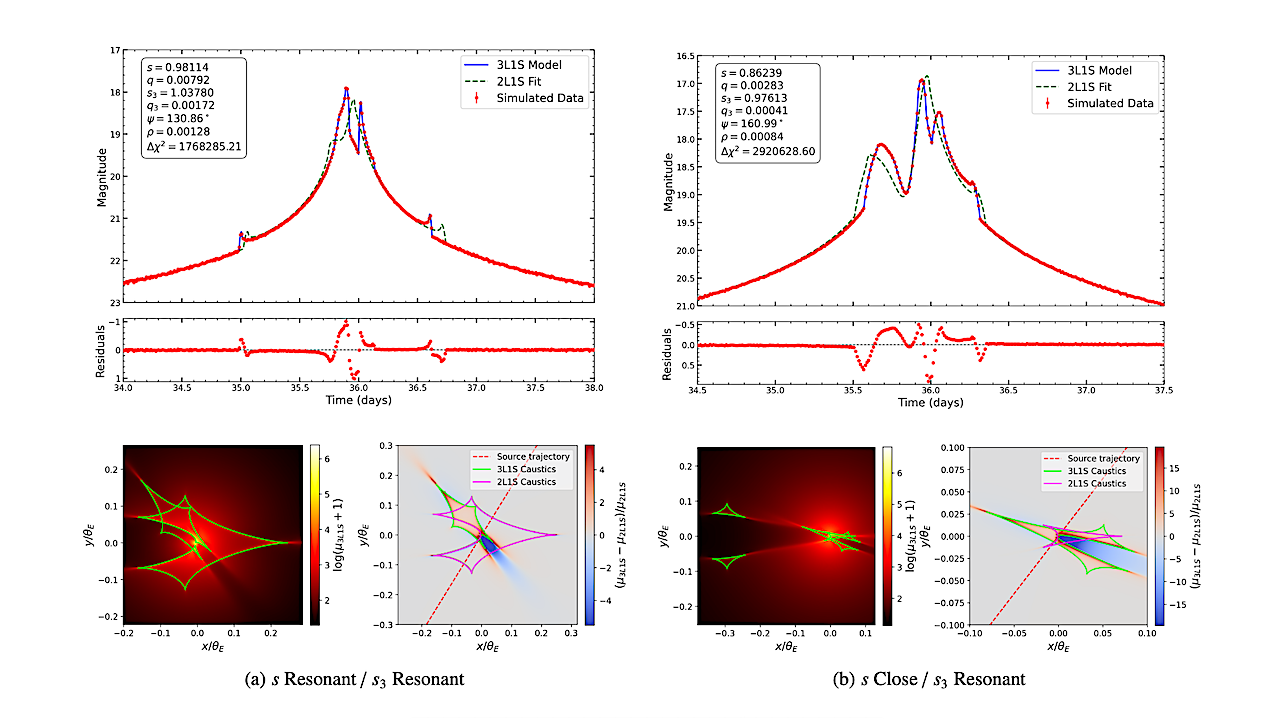
Recent astronomical discoveries are reshaping our understanding of the universe, revealing new cosmic phenomena and enhancing our knowledge of familiar celestial bodies. Researchers have made significant strides in deciphering the mysteries of dark matter, black holes, and planetary exploration, all contributing to an evolving picture of our cosmos.
Unmasking Cosmic Enigmas
One of the most astonishing findings is a mysterious object with a mass equivalent to one million suns, discovered in deep space. This entity defies classification as either a black hole or a star cluster, prompting astronomers to rethink existing theories about the formation and behavior of massive objects in the universe. Scientists are currently investigating its origins and characteristics to understand its role in cosmic evolution.
In another groundbreaking revelation, researchers have identified a hidden power source within a supermassive black hole. Evidence suggests that these gravitational giants are not merely consuming surrounding matter; they actively generate energy in unexpected ways. This discovery could redefine our understanding of the mechanisms powering some of the universe’s most energetic phenomena.
Exploring the Far Side of the Moon and Beyond
The Moon’s far side, always hidden from Earth, is now under scrutiny as scientists uncover unusual geological features that differ significantly from those on the near side. This revelation raises questions about the Moon’s history and composition, inviting further exploration to determine the nature of these differences.
Advancements in particle physics are bringing researchers closer to identifying the elusive nature of dark matter. Recent breakthroughs suggest new particle candidates and subtle cosmic fingerprints, potentially revealing the composition of this invisible substance that constitutes a substantial portion of the universe.
The James Webb Space Telescope continues to provide remarkable insights, including the detection of an atmosphere around a planet situated in the habitable zone of its star. These findings mark a significant step toward identifying potentially habitable worlds beyond our solar system.
Galactic Discoveries Illuminate the Universe
Astronomers have recently identified the most powerful and distant cosmic ring ever observed, a colossal structure that challenges previous notions of how such formations occur in the early universe. This discovery emphasizes the dynamic nature of the cosmos and the ongoing evolution of our understanding.
The Hubble Space Telescope has captured images of galaxies showcasing vibrant blue and gold hues, indicative of star formation. These colors signify a mix of young and older stars, providing a snapshot of a galaxy’s lifecycle. In another stunning observation, Hubble has documented a galaxy undergoing extreme gravitational forces, resulting in the birth of new stars amidst chaos.
In planetary science, a recent event involving a small asteroid passing over Antarctica without detection underscores the need for enhanced monitoring of near-Earth objects. This incident emphasizes the potential risks posed by unseen space debris and the importance of vigilance in planetary defense.
Meanwhile, the icy moon Enceladus has revealed further clues suggesting it could harbor the ingredients necessary for life. Analyzing data from the Cassini mission, scientists discovered organic molecules in the moon’s geysers, hinting at a potentially habitable environment beneath its icy surface.
The ongoing exploration of Mars continues to yield promising results. NASA’s Perseverance rover has found evidence suggesting that ancient lakes and rivers may have once existed on the planet, indicating it could have supported microbial life in the past. These findings are instrumental in understanding Mars’ geological history and its capacity for life.
As astronomers make strides in mapping the universe, a record-breaking radio halo, estimated to be 10 billion years old, has been discovered, reshaping theories regarding the early universe’s structure. Additionally, the largest-ever map of the universe has revealed ten times more early galaxies than previously thought, suggesting rapid galaxy formation in the cosmos.
These discoveries, alongside the confirmation of over 6,000 exoplanets by NASA, reflect the dynamic nature of space exploration. As scientists continue to investigate the myriad mysteries of the universe, each new finding adds depth to our understanding of cosmic phenomena and the potential for life beyond Earth.