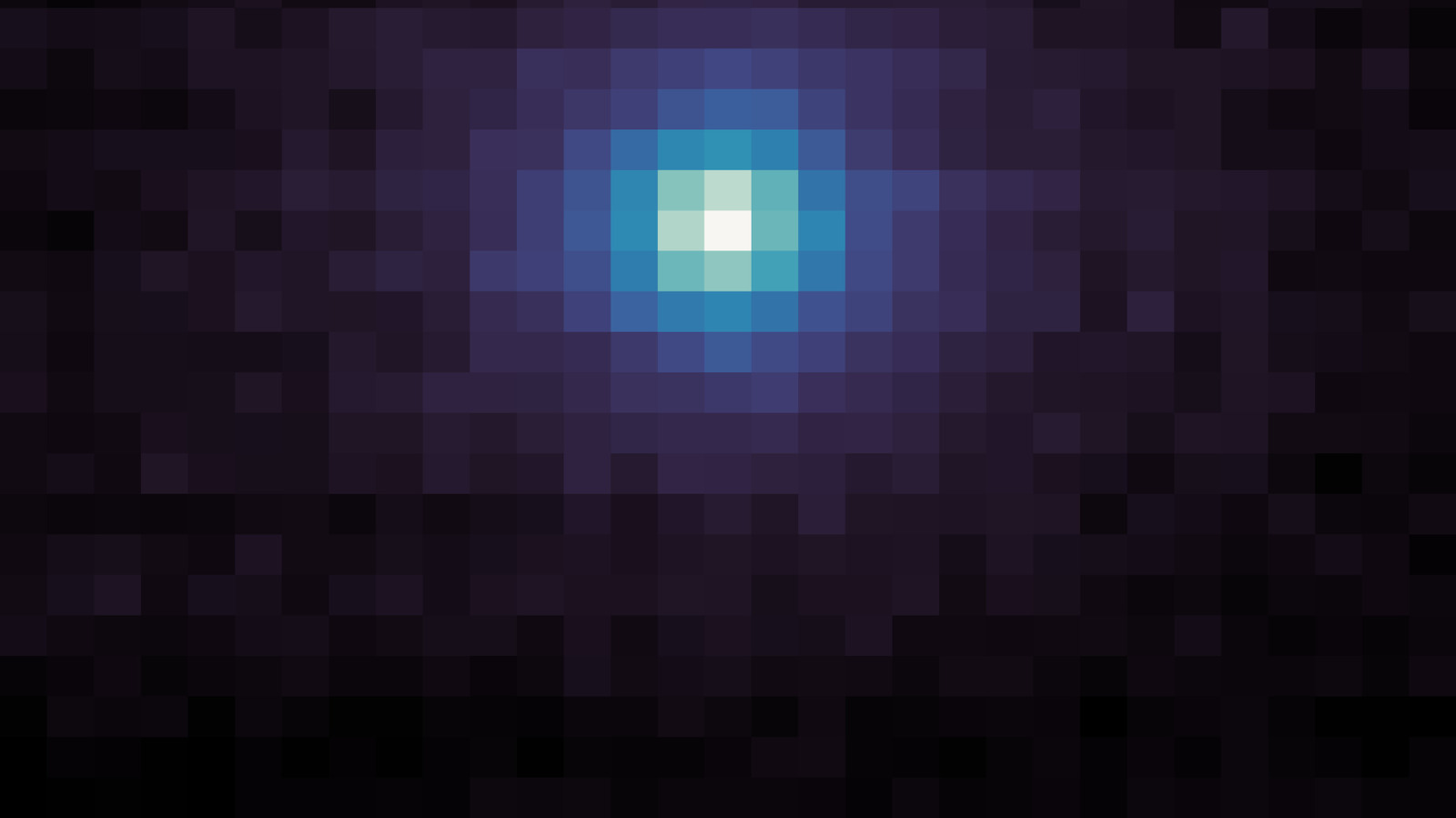
An international team of astronomers has made significant discoveries about the elliptical galaxy known as NGC 4486B using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). Their findings, published on December 16, 2023, on the arXiv preprint server, provide crucial insights into the galaxy’s unique double nucleus structure.
Located approximately 60 million light-years away in the Virgo constellation, NGC 4486B is a fascinating subject for study due to its distinct characteristics. The observational campaign leveraged the advanced capabilities of JWST to capture detailed images and data, revealing complexities within the galaxy’s dual cores that were previously difficult to discern.
Insights from the James Webb Space Telescope
The research team utilized JWST’s infrared technology to penetrate cosmic dust and gather information about the galaxy’s structure. This high-resolution imaging has allowed scientists to analyze the interactions between the two nuclei, shedding light on their formation and evolution. The dual nucleus is thought to result from a merger of smaller galaxies, a common occurrence in the universe.
Astronomers have identified various properties of the double nucleus, including its mass, brightness, and the distribution of stars around each core. The team reported that the two nuclei exhibit differing characteristics, suggesting that they may represent two distinct evolutionary paths. This nuanced understanding contributes to the broader knowledge of galaxy formation and the role of mergers in cosmic evolution.
The Significance of the Findings
The implications of this research extend beyond NGC 4486B itself. Understanding the dynamics of double nuclei helps astronomers refine their models of galaxy evolution, particularly in how galaxies interact and merge over billions of years. The data gathered from JWST could inform future studies on a range of topics, from star formation rates to the distribution of dark matter in galaxies.
As the JWST continues to explore the universe, it is expected to uncover more secrets about the cosmos. The findings related to NGC 4486B underscore the importance of international collaboration in astronomical research, enabling scientists to combine expertise and resources for a deeper understanding of the universe’s complexities.
In summary, the observational campaign on NGC 4486B marks a significant advancement in the study of galaxies, highlighting the potential of the James Webb Space Telescope to enhance our understanding of cosmic phenomena. This research not only enriches the scientific community but also captivates the imagination of those interested in the mysteries of the universe.